The structure blocks for GAAP is Accounting standards. The sum of the thoughts and rules in GAAP can be followed back to the concealed accounting principles.
This isn’t just holding some accounting information for a test and subsequently neglecting to recollect it two days afterward. These norms show up wherever in the examination of accounting.
Trust me. After you know the key accounting guidelines, most accounting subjects will look good. And also you can get some important points about Why accounting is so important? You will have the choice to reference these norms and reason your way through pay, cost, and some other blend of issues later on in the assessment course.
Key features
- Accounting standards are realized to improve the idea of cash related information uncovered by associations.
- In the United States, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) gives the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
- GAAP is required for all exchanges on open market associations in the U.S.; it is moreover consistently executed by non-exchanged on open market associations as well.
- IASB issues IFRS.
- The FASB and IASB at times participate to give joint standards on fascinating issue issues, anyway, there is no desire for the U.S. to change to IFRS in the foreseeable future.
- Once-over of compulsory guidelines of accounting.
Why Principles of Accountancy Important?
Sound accounting standards are significant on the grounds that they set the principles for announcing and accounting. These Principles of Accountancy regularly called the GAAP structure, keep up consistency in budgetary announcing from organization to organization overall ventures.
Keep in mind, the whole purpose of budgetary bookkeeping is to give valuable data to fiscal report clients. In the event that everybody detailed their budgetary data in an unexpected way, it is hard to think about organizations. Principles of Accountancy set the guidelines for detailing money related data, so everything organizations can be analyzed consistently.
What is the Purpose of Principles of Accountancy?
The reason for Principles of Accountancy is to build up the system for how monetary bookkeeping is recorded and covered fiscal reports.
At the point when each organization observes similar structure and rules, speculators, banks, and other budget summary clients will have a simpler time understanding the reports and settling on choices dependent on them.
Here are the ICAI Principles of Accountancy rules by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India. These rules are followed by the preparers and commentators of financial reports close by various accomplices.
- Disclosure of Accounting Policies – AS-1
- Valuation of Inventories – AS-2:
- Cash Flow Statements -AS-3
- Construction Accounting – AS-7
- Revenue Recognition -AS-9:
- Accounting for Fixed Assets -AS-10
- Employee Benefits -AS-15:
- Earnings per Share -AS-20
- Intangible Assets -AS-26
- Impairment of Assets – AS-28
Disclosure of Accounting Policies – AS 1
The First Principles of Accountancy is Disclosure of Accounting Policies. This standard plans with the introduction of basic accounting approaches which are proceeded in preparing and presenting spending rundowns.
Valuation of Inventories – AS 2
The second principle of Accountancy is the Valuation of Inventories. This standard game plans with the affirmation of huge worth at which inventories are passed on in the monetary outlines, including the ascertainment of cost of inventories and any record thereof to net practical worth.
Cash Flow Statements -AS 3
The third Principle of Accountancy is the cash flow statement. This standard game plans with the true changes in genuine cash and cash reciprocals of an undertaking.
This is done by setting up an attestation broadly called Cash Flow Statement. This attestation orders salaries during the period from working, contributing, and financing works out.
Construction Accounting – AS 4
This Standard courses of action with the treatment of conceivable outcomes and events occurring after the bookkeeping report date.
Net advantage or Loss for the Period, Prior Period Items and Changes in Accounting Policies (AS 5)
This Principles of Accountancy standard should be applied by an undertaking in presenting advantage or hardship from practices in the normal course of business, uncommon things and prior period things. This also recollects changes for accounting assessments and changes in accounting methodologies.
Improvement Contracts -AS 7
This Principles of Accountancy standard suggests the speaking to improvement contracts in the spending reports of impermanent laborers.
Pay Recognition – AS 9
This Principles of Accountancy game plans with the affirmation of pay in Profit and Loss a/c of an endeavor. Pay affirmation is stressed over the pay arising all through the normal activities of the endeavor, for instance, the proposal of product, conveying of organizations, interest, sways, and benefits.
Property, Plant and Equipment – AS 10
The objective of this Standard is to underwrite the accounting treatment for property, plant and stuff (PPE).
The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates – AS 11
AS 11 sets down guidelines of speaking to new money trades and new exercises, i.e., which trading scale to utilize and how to see the cash related effect of exchange rates changes.
Government Grants – AS 12
This standard plans with speaking to government grants. These are from time to time called enrichments, cash inspirations, commitment drawbacks, etc.
Speaking to Investments- AS 13
This Principles of Accountancy standard plans with speaking to interests in the spending rundowns of adventures and related disclosure essentials.
Speaking to Amalgamations -AS 14
This standard game plans with speaking to combinations and the treatment of any resultant liberality or stores.
Agent Benefits -AS 15
The objective of this standard is to support the accounting treatment and disclosure for delegate preferences in the books of a business beside specialist share-based portions. It doesn’t oversee accounting and uncovering by laborer advantage plans.
Getting Costs -AS 16
This standard should be applied in speaking to getting costs. It doesn’t deal with the certifiable or credited expense of owners’ worth, including tendency offer capital not named a danger.
Giving a record of cash related segments – AS 17
The Principles of Accountancy of this standard is to develop norms for specifying cash related information for different sorts of areas, things, organizations, and undertaking produces and the unmistakable geological locales in which it works.
Disclosure of related assembling trades – AS 18
This standard should be applied in declaring related assembling trades between an itemizing undertaking. The standard applies to the spending rundowns of each noteworthy undertaking and moreover to the joined monetary reports presented by a holding association.
Accounting approaches and disclosure on Lease trades – AS 19
The Principles of Accountancy objective of this standard is to suggest the fitting accounting techniques and presentations as per back leases and working leases.
Earnings Per Share – AS 20
AS 20 supports principles for the affirmation and presentation of benefit per share which will improve the assessment of execution among different endeavors for a comparable accounting period and among different accounting periods for a comparable undertaking.
Preparation and Presentation of Consolidated Financial Statements – AS 21
The objective of this standard is to set down guidelines and techniques for game plan and presentation of consolidated spending reports. Joined spending outlines are fated to present budgetary information about a parent and its helpers as a single financial component.
This is done to show the budgetary resources obliged by the substance when all is said in done, duties of the social event and results in the get-together achieves with its resources.
Speaking to Taxes on Income- AS 22
The Principles of Accountancy objective of this Standard is to underwrite the accounting treatment of obligations on pay since the accessible compensation may be in a general sense special comparable to the compensation that appeared in monetary reports in light of various reasons, introducing issues in organizing of charges against pay for a period.
Speaking to Investments in Associates – AS 23
This Principles of Accountancy standard should be applied in speaking to interests in accomplices in the status and presentation of set Financial Statements (CFS) by a theorist.
Halting Operations – AS 24
The objective of AS 24 is to set up principles for declaring information about completion errands.
This enables the customers of spending synopses to make a measure of an undertaking’s livelihoods, to benefit creating cutoff, and cash related circumstance by secluding information about stopping assignments and continuing with exercises. This accounting standard applies to all suspending assignments of an endeavor.
Break Financial Reporting -AS 25
This Principles of Accountancy standard applies if a substance is required or decides to disseminate a span budgetary report. The prime objective of this standard is to suggest the base substance of a break budgetary report. This standard moreover suggests the norms for affirmation and assessment of spending rundowns for a span period.
Unimportant Assets-AS 26
AS 26 embraces the accounting treatment for slippery assets. Insignificant assets imply non-monetary assets which are unmistakable, without genuine substance, held for use in the creation or nimbly of items, organizations, administrative explanation, and so on
Joint Ventures uncovering of interest in Financial verbalizations -AS 27
The objective of AS 27 is to set out the principles and strategies for speaking to interests in joint undertakings and declaring of experience assets, liabilities, pay and expenses in the spending reports of experiences and budgetary pros.
Shortcoming of Assets -AS 28
The objective of AS 28 is to support the procedures that an undertaking applies to ensure that its assets are passed on at near their recoverable whole.
The asset can be represented as hindered if it’s passing on whole outperforms the aggregate to be recovered through use or offer of the asset and it requires the business substances to see an inability setback in such cases.
Unforeseen Liabilities and Contingent Assets and Provisions -AS 29
The objective of AS 29 is to ensure that fitting affirmation principles and assessment bases are applied to courses of action and unanticipated liabilities.
This ensures that sufficient information is uncovered in the notes to the spending reports which enable customers to grasp their tendency, timing, and entirety. The objective here is in like manner to set down legitimate speaking to unexpected assets.
Rundown of ICAI’s Non-Mandatory Accounting Standards (AS 30~32)
ICAI has declared on 15 Nov. 2016 that ‘AS 30-Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement’, ‘AS 31-Financial Instruments: Presentation’, ‘AS 32-Financial Instruments: Disclosures’ stands removed
ICAI announced eliminated the going with accounting rules:
AS 30 – Financial Instruments Recognition and Measurement
AS 31-Financial Instruments Presentation
Principles of Accountancy Glance
| Accounting Standard (AS) | Title of the AS |
| AS 1 | Disclosure of Accounting Policies |
| AS 2 | Valuation of Inventories |
| AS 3 | Cash Flow Statements |
| AS 4 | Contingencies and Events Occurring After the Balance Sheet Date |
| AS 5 | Net Profit or Loss for the Period, Prior Period Items and Changes in Accounting Policies |
| AS 6 | Depreciation Accounting |
| AS 7 | Construction Contracts |
| AS 8 | Accounting for Research and Development |
| AS 9 | Revenue Recognition |
| AS 10 | Accounting for Fixed Assets |
| AS 11 | The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates |
| AS 12 | Accounting for Government Grants |
| AS 13 | Accounting for Investments |
| AS 14 | Accounting for Amalgamations |
| AS 15 | Employees Benefits (Revised 2005) |
| AS 16 | Borrowing Costs |
| AS 17 | Segment Reporting |
| AS 18 | Related Party Disclosures |
| AS 19 | Leases |
| AS 20 | Earnings Per Share |
| AS 21 | Consolidated Financial Statements |
| AS 22 | Accounting for Taxes on Income |
| AS 23 | Accounting for Investments in Associates in Consolidated Financial Statements |
| AS 24 | Discontinuing Operations |
| AS 25 | Interim Financial Reporting |
| AS 26 | Intangible Assets |
| AS 27 | Financial Reporting of Interests in Joint Ventures |
| AS 28 | Impairment of Assets |
| AS 29 | Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets |
| AS 30 | Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement |
| AS 31 | Financial Instruments: Presentation |
| AS 32 | Financial Instruments: Disclosures |
Fundamental Principles of Accountancy
Coming up next is a rundown of the ten fundamental Principles of Accountancy and rules along with an exceptionally dense clarification of each.
- Recorded Cost Principle
- Income Recognition Principle
- Coordinating Principle
- Total honesty Principle
- Money saving advantage Principle
- Objectivity Principle
- Traditionalism Principle
- Consistency Principle
- Going Concern Principle
- Materiality
Recorded Cost Principle
Authentic Cost Principle – expects organizations to record the acquisition of products, administrations, or capital resources at the value they paid for them.
Resources are then stayed on the monetary record at their verifiable without being changed for variances in market esteem.
Income Recognition Principle
Income Recognition Principle – expects organizations to record income when it is acquired rather than when it is gathered. This accumulation premise of bookkeeping gives a more exact image of money related occasions during the period.
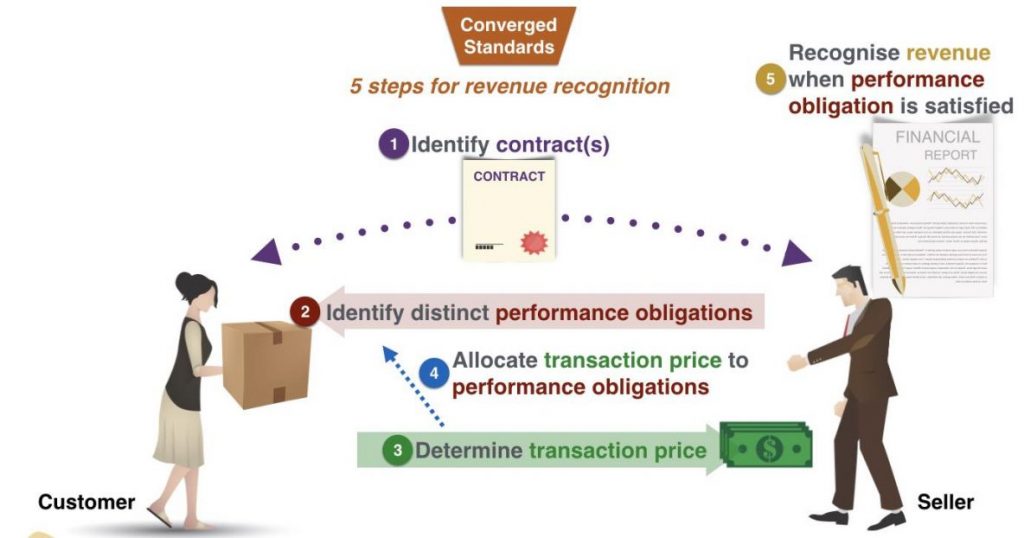
Under the gathering premise of bookkeeping (rather than the money premise of bookkeeping), incomes are perceived when an item has been sold or an assistance has been performed, paying little mind to when the cash is really gotten.
Coordinating Principle
Coordinating Principle – states that all costs must be coordinated and recorded with their separate incomes in the period that they were brought about rather than when they are paid.
This guideline works with the income acknowledgment standard guaranteeing all income and costs are recorded on the accumulation premise.
This accounting rule anticipates that associations should use the amassing reason for accounting. The planning decision requires that expenses be composed of livelihoods.
Total honesty Principle
Total honesty Principle – necessitates that any information that would really influence a fiscal report client’s choice about the organization must be unveiled in the references of the budget summaries.
This shields association from disguising material real factors about accounting practices or known conceivable outcomes later on.
Money saving advantage Principle
Money-saving advantage Principle – limits the necessary measure of exploration and time to record or report budgetary data if the expense exceeds the advantage.
Along these lines, if recording an irrelevant occasion would cost the organization a material measure of cash, it ought to be done without.
Traditionalism Principle
Traditionalism Principle – bookkeepers ought to consistently mistake on the most moderate side conceivable in any circumstance. This keeps bookkeepers from over assessing future incomes and thought little of future costs that could misdirect budget summary clients.
In the event that a circumstance emerges where there are two adequate choices for revealing a thing, traditionalism guides the bookkeeper to pick the elective that will bring about less net gain or potentially less resource sum.
Traditionalism encourages the bookkeeper to “break a tie.” It doesn’t immediate bookkeepers to be moderate. Bookkeepers are relied upon to be unprejudiced and objective.
The fundamental Principles of Accountancy rule of traditionalism drives bookkeepers to foresee or unveil misfortunes, however, it doesn’t permit a comparable activity for gains.
Objectivity Principle
Objectivity Principle – budget summaries, bookkeeping records, and money related data all in all should be autonomous and liberated from predisposition.
The fiscal reports are intended to pass on the money related situation of the organization and not to convince end clients to make certain moves.
Consistency Principle
All accounting principles and speculations should be applied dependably beginning with one period then onto the following.
This ensures that financial reports are identical among periods and all through the association’s arrangement of encounters.
Going Concern Principle
This bookkeeping rule expects that an organization will keep on existing long enough to complete its destinations and responsibilities and won’t sell within a reasonable time-frame.
On the off chance that the organization’s monetary circumstance is with the end goal that the bookkeeper accepts the organization won’t have the option to forge ahead, the bookkeeper is needed to reveal this appraisal.
The going concern guideline permits the organization to concede a portion of its prepaid costs until future bookkeeping periods.
Materiality
As a result of this fundamental bookkeeping standard or rule, a bookkeeper may be permitted to disregard another bookkeeping guideline if a sum is irrelevant. Capable judgment is required to pick whether an entirety is irrelevant or inconsequential.
Because of materiality, spending reports customarily show aggregates changed in accordance with the nearest dollar, to the nearest thousand, or to the nearest million dollars depending upon the size of the association.